The principle of an adiabatic air cooler
An adiabatic air cooler uses evapotranspiration technology. Used for a long time in hot and dry countries, this evaporative cooling system is economical and ecological. This technology reproduces the phenomenon of evaporation observed near a water source in summer. The hot, dry air passing through the wet heat exchanger is cooled. The energy used by the evaporation of water is taken from the air. The air is then cooled. This conversion is called adiabatic, i.e. constant enthalpy. It neither adds nor gains heat and therefore energy.
How an adiabatic air cooler works
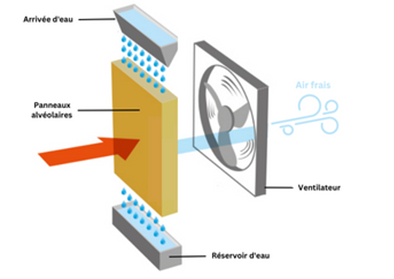
The operation of an adiabatic air cooler is 100% natural and ecological: cooling by evaporation. The unit draws in warm air from a room. The air drawn in by the unit passes through honeycomb panels, humidified by a water tank. When it comes into contact with the calories contained in the ambient air, the water evaporates and causes a drop in temperature. The air leaving the unit is therefore fresh. Unlike air conditioning, the adiabatic air cooler uses no refrigerant.
For the proper operation of the adiabatic air cooler, a power source and water supply is essential. The water is taken by a pump immersed in the tank. It then flows through the heat exchanger to cool the air. The tank is also equipped with a UV lamp for water treatment.
The use of an adiabatic air cooler
Using an adiabatic air cooler is easy. It is important to fill the tank with fresh water. Then, simply plug the device into the mains and press the “on” button. You can then set the speed and the adjustment vanes.
Examples of applications
Adiabatic air coolers are suitable for industrial applications. Possible applications are as follows :
Pharmaceutical products
For an optimal conservation of the drugs.
Garment factory
Very comfortable temperature and fast and continuous removal of smoke and odors.
Automotive sector
Provide a comfortable temperature for customers and employees. Eliminates off-gassing often caused by volume shrinkage.
Foundries
Reduce heat and smoke in the plant.
Machine room or datacenter
Solve overheating problems and improve the efficiency of turbomachinery or internal combustion engines.
Food industry
Fruits and vegetables retain their freshness and value because the high humidity in the environment minimizes weight loss.
Electronic components
Static electricity is a threat to modern electronic circuits. Controlled humidity levels will keep the work area free of electrostatic discharge problems.
Paper/Cardboard Mills
The packaging will not break under appropriate relative humidity. The temperature of the staff very pleasant.
Flour plant
The seeds are fed by air. This air extracted from the room can cause grinding difficulties when it is too dry. During packaging, paper bags may burst due to insufficient atmospheric humidity.
Packaging or other product manufacturing plants
Eliminates dust, particles and insects that can become embedded in the product, providing a very comfortable room temperature for workers.
Metallurgy sector plant
Heat from machines, ovens… as well as fumes and gases are eliminated. Increase productivity with comfortable temperatures. Machines and tools operate accurately when the ambient temperature is correct.
Wood industry
Maintains the moisture content of the wood at a level that allows for stability and easy handling consistency at minimal cost. High humidity has the added benefit of reducing static electricity and dust, as well as a more comfortable working environment.
Paint applications :
Proper temperature and moisture content will maintain the strength of the paper and make it less brittle. Paper that is too dry tends to be statically charged and is difficult to handle. When a constant level of humidity is maintained during printing, the paper retains its properties, reducing the risk of errors and saving printing inks.
Graphic Art
Proper temperature and moisture content will maintain the strength of the paper and make it less brittle. Paper that is too dry tends to be statically charged and is difficult to handle. When a constant level of humidity is maintained during printing, the paper retains its properties, reducing the risk of errors and saving printing inks.
Agrarian sector
Losses due to overheating are avoided. Raise and breed in an ideal environment for animals, free of bad odors and insects. The yield has increased. Engine room or combined heat and power generation, solving problems caused by overheating and increasing the efficiency of turbines or internal combustion engines.




Laisser un commentaire